CHOW is a new kind of emerging food media. Not only is their subject matter different, but they deliver it to you in audio, video, and everything else the Web's got to offer. CHOW offers recipes, instruction, news, entertainment, discussion, and advice.
CHOW Tips are a series of succinct instructional videos. Each video is concise, to the point, and has a running time of approximately 30 seconds, which doesn’t leave a lot of time to cover a surprising breadth of subject matter. However, the skill levels addressed here is quite impressive.
The CHOW Tips featured on Watch Foodie Network are the best and most relevant in their respective categories that CHOW has to offer. In a matter of speaking, we did all the heavy sifting so that you won't have to.
We start off our CHOW Tips with Healthy Diet & Nutrition videos; just click on Show More  .
.
Bon appétit.
Healthy Diet & Nutrition
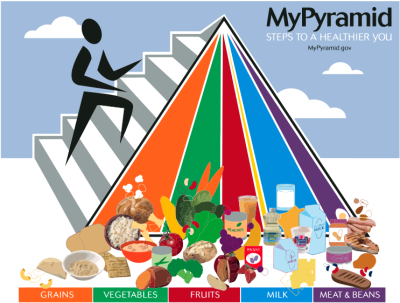
A healthy diet is one that helps maintain or improve health. It is important for lowering many chronic health risks, such as obesity, heart disease, diabetes, hypertension and cancer, A healthy diet involves consuming appropriate amounts of all essential nutrients and an adequate amount of water.
Nutrients can be obtained from many different foods, so there are numerous diets that may be considered healthy. A healthy diet needs to have a balance of macronutrients (fats, proteins, and carbohydrates), calories to support energy needs, and micronutrients to meet the needs for human nutrition without inducing toxicity or excessive weight gain from consuming excessive amounts.
There are a number of diets and recommendations by numerous medical and governmental institutions that are designed to promote certain aspects of health.
The World Health Organization (WHO) makes the following recommendations with respect to both populations and individuals:
- Achieve an energy balance and a healthy weight.
- Limit energy intake from total fats and shift fat consumption away from saturated fats to unsaturated fats and towards the elimination of trans-fatty acids.
- Increase consumption of fruits and vegetables, legumes, whole grains and nuts.
- Limit the intake of simple sugar. A 2003 report recommends less than 10% simple sugars.
- Limit salt / sodium consumption from all sources and ensure that salt is iodized.
- Sufficient essential amino acids ("complete protein") to provide cellular replenishment and transport proteins. All essential amino acids are present in animals. Some plants (such as quinoa, soy and hemp) give all the essential acids. A combination of other plants in a diet may also provide all essential amino acids. Fruits such as avocado and pumpkin seeds also have all the essential amino acids.
- Essential micronutrients such as vitamins and certain minerals.
- Avoiding foods contaminated by human pathogens (e.g. E. coli, tapeworm eggs).
 The American Heart Association recommends a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, healthful fatty acids and limited saturated fat.
The American Heart Association recommends a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, healthful fatty acids and limited saturated fat.
In addition to dietary recommendations for the general population, there are many specific diets that have primarily been developed to promote better health in specific population groups, such as people with high blood pressure (as in low sodium diets or the more specific DASH diet), or people who are overweight or obese (in weight control diets). However, some of them may have more or less evidence for beneficial effects in normal people as well.
A comprehensive worldwide report, Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity and the Prevention of Cancer: a Global Perspective, compiled by World Cancer Research Fund and American Institute for Cancer Research, reports that there is significant relation between lifestyle (including food consumption) and cancer prevention. The same report recommends eating mostly foods of plant origin and aiming to meet nutritional needs through diet alone, while limiting consumption of energy-dense foods, red meat, alcoholic drinks and salt and avoiding sugary drinks, and processed meat.
An unhealthy diet is a major risk factor for a number of chronic diseases including: high blood pressure, diabetes, abnormal blood lipids, overweight/obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. The WHO estimates that 2.7 million deaths are attributable to a diet low in fruit and vegetable every year. Globally it is estimated to cause about 19% of gastrointestinal cancer, 31% of ischemic heart disease, and 11% of strokes, thus making it one of the leading preventable causes of death worldwide.
Grocery School:
A supermarket, a form of grocery store, is a self-service store offering a wide variety of food and household merchandise, organized into departments. It is larger in size and has a wider selection than a traditional grocery store, also selling items typically found in a convenience store, but is smaller and more limited in the range of merchandise than a hypermarket or big-box store.
The supermarket typically comprises meat, fresh produce, dairy, and baked goods departments, along with shelf space reserved for canned and packaged goods as well as for various non-food items such as household cleaners, pharmacy products and pet supplies. Most supermarkets also sell a variety of other household products that are consumed regularly, such as alcohol (where permitted), medicine, and clothes, and some stores sell a much wider range of non-food products.
The traditional suburban supermarket often presents elaborate in-store displays of products. The stores are usually part of corporate chains that own or control (sometimes by franchise) other supermarkets located nearby—even transnationally—thus increasing opportunities for economies of scale. Supermarkets typically are supplied by the distribution centres of their parent companies, usually in the largest city in the province.
Supermarkets usually offer products at low prices by reducing their economic margins. Certain products (typically staple foods such as bread, milk and sugar) are occasionally sold as loss leaders, that is, with negative profit margins. To maintain a profit, supermarkets attempt to make up for the lower margins by a higher overall volume of sales, and with the sale of higher-margin items. At present, many supermarket chains are attempting to further reduce labor costs by shifting to self-service check-out machines, where a single employee can oversee a group of four or five machines at once, assisting multiple customers at a time.
A larger full-service supermarket combined with a department store is sometimes known as a hypermarket. Other services offered at some supermarkets may include those of banks, cafés, childcare centres/creches, photo processing, video rentals, pharmacies and/or petrol stations.
Whilst branding and store advertising will differ from company to company, the layout of a supermarket remains virtually unchanged. Although big companies spend time giving consumers a pleasant shopping experience, the design of a supermarket is directly connected to the in-store marketing that supermarkets must conduct in order to get shoppers to spend more money whilst there.
Every facet of the store is mapped out and attention is paid to color, wording and even surface texture. The overall layout of a supermarket is a visual merchandising project that plays a major role in retailing. Stores can creatively use a layout to alter customers’ perceptions of the atmosphere. Alternatively, they can enhance the store’s atmospherics through visual communications (signs and graphics), lighting, colors, and even scents. For example, to give a sense of the supermarket being healthy, fresh produce is deliberately located at the front of the store.
 |
BEER: 3 ways to chill beer, how to pair beer with food, how to identify off flavors in beer, and more. |
 |
WINE: The best cheap wines, how to properly chill wine, wine tasting, wine paIring, and more. |
 |
SPIRITS: How to taste fine spirits, when to blow on your liquor, how to make the perfect martini and more. |
 |
MEAT & POULTRY: How to choose fresh meat, how to grill, how to make the perfect hamburger, and more. |
 |
SEAFOOD: 22 back-of-the-house secrets from chefs, such as how to buy fresh fish, and how to smoke or grill seafood. |
 |
PRODUCE: Tips that will help you get your daily recommended servings of grains, cereals, fruits, and vegetables. |
 |
CHEESE: How to buy cheese, how to cut and serve cheese, whether or not to freeze cheese, and more. |
 |
COFFEE: Banish bitter coffee from your repertoire. CHOW Tips will help brew a delicious cup every time. |
Contact Us | Shop | Sitemap | Join Our Team | Investors | Advertise | Web Design Services
Community | Foodies' Choice | Meetup Groups | Chat | Blogs | Forums | Submit Your Site | Resources
